Background
Fine chemical wastewater is a typical type of toxic/difficult-to-degrade industrial organic wastewater characterized by high COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand), high ammonia nitrogen, and high color. The main components harmful to microorganisms in this wastewater are COD, ammonia nitrogen, heavy metal ions, dyes, and their decomposition products, especially organic pollutants. The organic components in fine chemical wastewater are mostly toxic/difficult-to-degrade organic pollutants, which exert significant inhibitory effects on biological systems, leading to non-compliant discharge as the primary reason.
Pain points
MVR (Mechanical Vapor Recompression) and multi-effect evaporation technology are utilized in various fields such as fine chemicals, hazardous waste disposal, food processing, papermaking, pharmaceuticals, and wastewater treatment. They are relatively energy-efficient methods for evaporation, concentration, and crystallization processes and are widely used. However, they encounter challenges related to the disposal of concentrated mother liquor generated during operation, leading to high costs. There are three main pain points:
- Re-injection of concentrated mother liquor into the original solution: Accumulation and enrichment of high-boiling-point organic compounds in the mother liquor result in an increase in the boiling point of wastewater. Consequently, it becomes more difficult to treat, leading to low evaporation efficiency, high operating costs, and in severe cases, equipment breakdown.
- Incineration of concentrated mother liquor: This method requires significant initial investment, and combustion burner heads are prone to clogging. It also consumes large amounts of fuel, leading to economic inefficiency and air pollution from exhaust emissions.
- Direct outsourcing of hazardous waste disposal: The cost of disposal is very high when directly outsourced, contributing to economic challenges in handling the concentrated spent liquor.
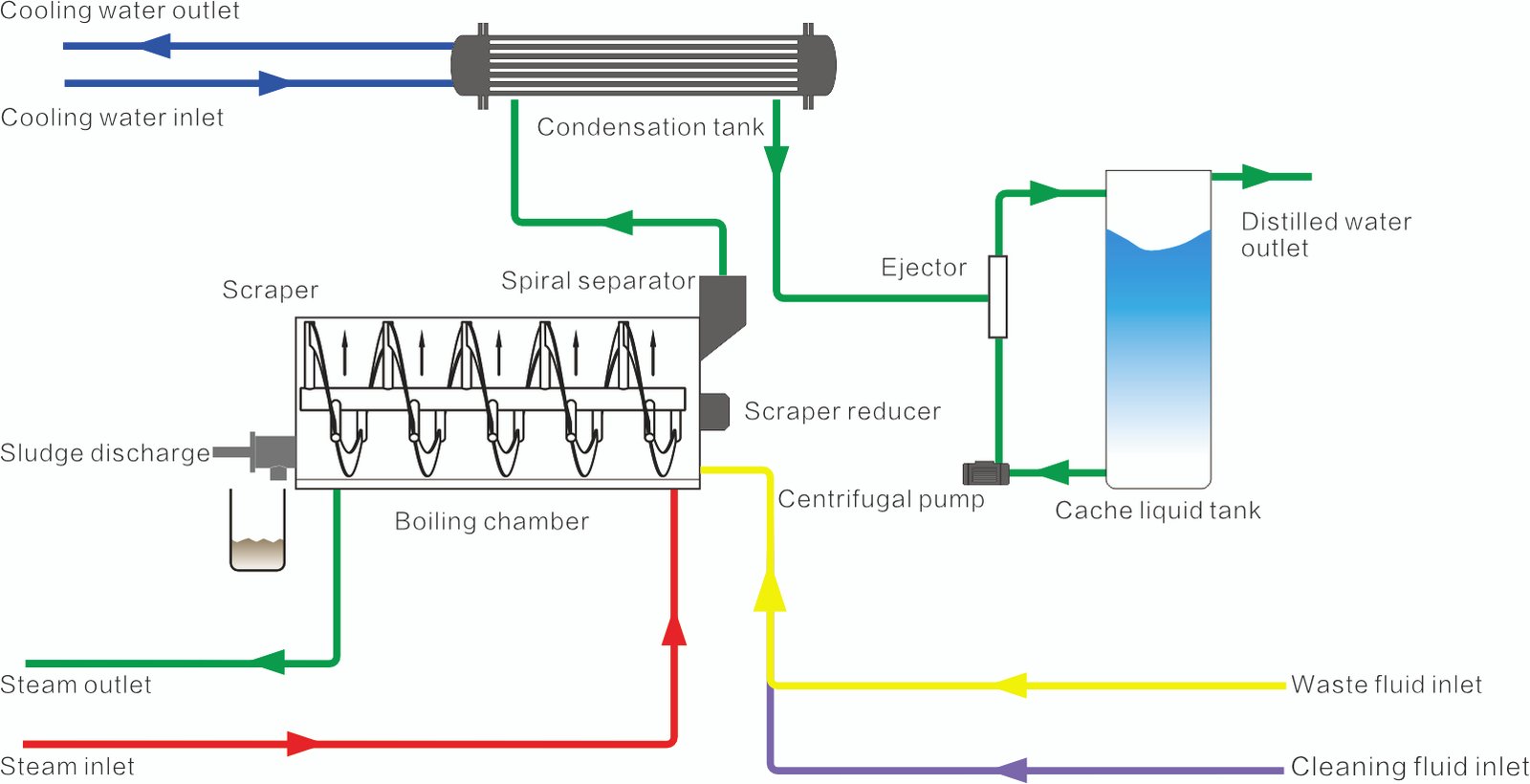
WSD’s Solution
To address the disposal challenges of concentrated mother liquor in the fine chemical industry, WSD has devoted years of research and innovation to develop a process that minimizes the volume of concentrated mother liquor. The process adopts Miller plate heat exchange technology, with a vacuum degree in the evaporation chamber maintained at -95 to -97 kPa, and the evaporation temperature generally kept between 40 to 45°C. Inside the evaporation chamber, a spiral scraper agitation is employed to ensure uniform heating. Additionally, the heating effect is enhanced by setting up agitation around the periphery, thereby improving the dryness of the discharged material.
Advantages
1. It operates without generating harmful gas emissions or thermal pollution.
2. The system features fully automated control for seamless operation.
3. Its design is standardized, modular, and skid-mounted for easy installation and maintenance.
4. The evaporator includes automatic discharge and cleaning functions to enhance efficiency.
5. It is equipped with cloud platform management for remote monitoring and control.
6. The system supports companies in achieving zero discharge.