Background
Coal chemical wastewater treatment refers to the process of treating wastewater generated during coal chemical production, which contains organic and inorganic pollutants, to meet national emission standards. Coal chemical wastewater contains toxic and harmful substances such as phenols, cyanides, oils, and sulfur, making it difficult to treat.
Coal chemical wastewater is mainly divided into two categories: organic wastewater and saline wastewater. Organic wastewater includes gasification wastewater (which accounts for over 60%), chemical plant wastewater, surface runoff water, initial rainwater, and domestic sewage. Its characteristics include high concentrations of COD and ammonia nitrogen, as well as a complex composition of salt ions. Saline wastewater includes wastewater that meets biological treatment standards and clean wastewater, with total dissolved solids (TDS) content ranging from 1 to 3 g/L. Saline wastewater further comprises low-salt wastewater, concentrated salt wastewater, and highly concentrated salt wastewater.
Pain points
Currently, the treatment of coal chemical end-of-pipe brine mainly relies on two technologies: “membrane concentration + evaporation crystallization to prepare mixed salts” and “membrane separation + evaporation crystallization and fractionation”. However, in the final evaporation crystallization stage, traditional tubular evaporators have been plagued by the presence of mixed salt mother liquor, which has been a persistent issue in the zero discharge treatment process for coal chemical wastewater. This mixed salt mother liquor exhibits the following characteristics:
- Large volume generation, typically 5-10% of the front-end evaporation system.
- “Four highs and one low,” namely “high COD, high color, high toxicity, high salinity, low B/C ratio,” making it difficult to biodegrade and degrade.
- High water content, making it difficult for traditional evaporators to further concentrate and crystallize, and difficult to be used as waste salt for resource heat treatment.
- Long-term recycling within the system leads to reduced efficiency of the evaporator, frequent cleaning, and even paralysis.
- Long-term circulation without discharge leads to changes in the water quality of the evaporation and crystallization device, affecting the quality of the front-end by-products such as color, TOC, etc.
- High cost and high risk when outsourced as hazardous waste.
- High environmental risk, easily disrupting the ecological balance.
Current traditional mother liquor disposal devices such as single-effect/single-vessel/rake drying/drum drying are used in the industry. However, based on actual application results, they fail to meet the demand for drying this mixed salt mother liquor and bring new operational challenges to customers, such as:
- Unable to achieve drying.
- High equipment failure rate, prone to paralysis.
- Frequent cleaning, poor on-site hygiene environment.
- Overall disposal efficiency is low, with high energy consumption and low automation level.
WSD’s Solution
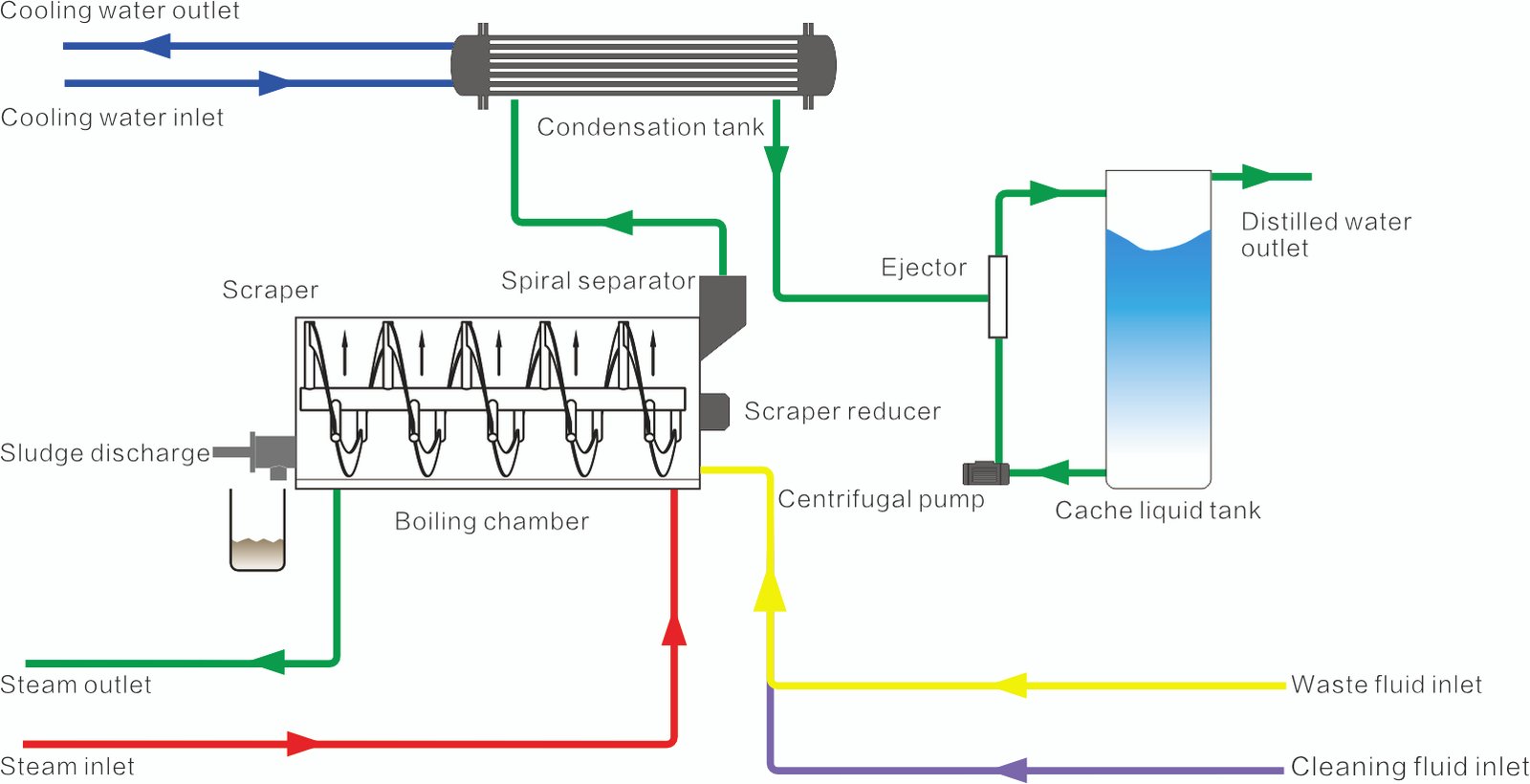
To address the challenge of drying mixed salt mother liquor in coal chemical end-of-pipe treatment, WSD Environmental Protection has dedicated years of research and innovation to develop a process that maximizes the drying of mixed salt mother liquor. The process adopts Miller plate heat exchange technology, with a vacuum degree in the evaporation chamber maintained at -95 to -97 kPa, and the evaporation temperature generally kept between 40 to 45°C. Inside the evaporation chamber, a spiral scraper agitation is employed to ensure uniform heating. Additionally, heating around the periphery of the agitation enhances heat transfer efficiency, improving the dryness of the discharged material.
Advantages
1. It operates without generating harmful gas emissions or thermal pollution.
2. The system features fully automated control for seamless operation.
3. Its design is standardized, modular, and skid-mounted for easy installation and maintenance.
4. The evaporator includes automatic discharge and cleaning functions to enhance efficiency.
5. It is equipped with cloud platform management for remote monitoring and control.
6. The system supports companies in achieving zero discharge.